From The University of Rochester
2.16.23
Bob Marcotte
bmarcotte@ur.rochester.edu

A perovskite crystalline stone isolated on white background. Perovskites, like the one shown here, show great potential as light-absorbing material for solar harvesting. (Getty Images photo)
The secret-a University of Rochester optics professor explains-is to harness the power of metals.
Silicon, the standard semiconducting material used in a host of applications—computer central processing units (CPUs), semiconductor chips, detectors, and solar cells—is an abundant and naturally occurring material. However, it is expensive to mine and to purify.
Perovskites—a family of materials nicknamed for their crystalline structure—have shown extraordinary promise in recent years as a far less expensive, equally efficient replacement for silicon in solar cells and detectors. Now, a study led by Chunlei Guo, a professor of optics at the University of Rochester, suggests perovskites may become far more efficient.
Researchers typically synthesize perovskites in a wet lab, and then apply the material as a film on a glass substrate and explore various applications
Guo instead proposes a novel, physics-based approach. By using a substrate of either a layer of metal or alternating layers of metal and dielectric material—rather than glass—he and his coauthors found they could increase the perovskite’s light conversion efficiency by 250 percent.
Their findings are reported in Nature Photonics [below].
“No one else has come to this observation in perovskites,” Guo says. “All of a sudden, we can put a metal platform under a perovskite utterly changing the interaction of the electrons within the perovskite. Thus, we use a physical method to engineer that interaction.”
Novel perovskite-metal combination creates ‘a lot of surprising physics’
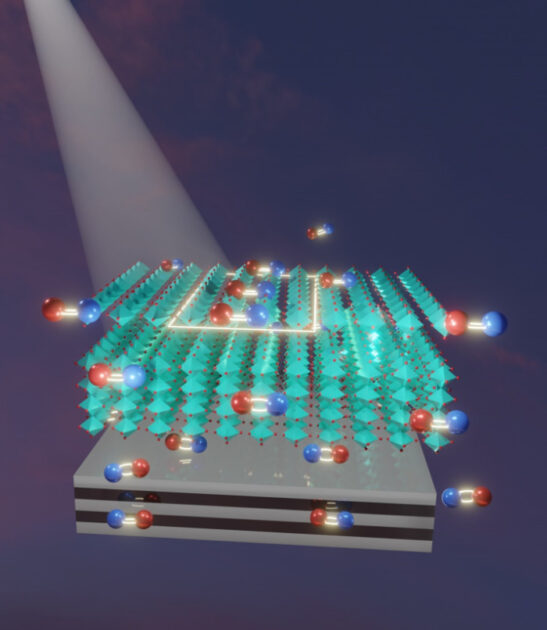
This illustration from the Guo Lab shows the interaction between a perovskite material (cyan) and a substrate of metal-dielectric material. The red and blue pairings are electron-hole pairs. Mirror images reflected from the substrate reduce the ability of excited electrons in the perovskite to recombine with their atomic cores, increasing the efficiency of the perovskite to harvest solar light. (Illustration by Chloe Zhang)
Metals are probably the simplest materials in nature, but they can be made to acquire complex functions. The Guo Lab has extensive experience in this direction. The lab has pioneered a range of technologies transforming simple metals to pitch black, superhydrophilic (water-attracting), or superhydrophobic (water-repellent). The enhanced metals have been used for solar energy absorption and water purification in their recent studies.
In this new paper, instead of presenting a way to enhance the metal itself, the Guo Lab demonstrates how to use the metal to enhance the efficiency of pervoskites.
“A piece of metal can do just as much work as complex chemical engineering in a wet lab,” says Guo, adding that the new research may be particularly useful for future solar energy harvesting.”
In a solar cell, photons from sunlight need to interact with and excite electrons, causing the electrons to leave their atomic cores and generating an electrical current, Guo explains. Ideally, the solar cell would use materials that are weak to pull the excited electrons back to the atomic cores and stop the electrical current.
Guo’s lab demonstrated that such recombination could be substantially prevented by combining a perovskite material with either a layer of metal or a metamaterial substrate consisting of alternating layers of silver, a noble metal, and aluminum oxide, a dielectric.
The result was a significant reduction of electron recombination through “a lot of surprising physics,” Guo says. In effect, the metal layer serves as a mirror, which creates reversed images of electron-hole pairs, weakening the ability of the electrons to recombine with the holes.
The lab was able to use a simple detector to observe the resulting 250 percent increase in efficiency of light conversion.
Several challenges must be resolved before perovskites become practical for applications especially their tendency to degrade relatively quickly. Currently, researchers are racing to find new, more stable perovskite materials.
“As new perovskites emerge, we can then use our physics-based method to further enhance their performance,” Guo says.
Coauthors include Kwang Jin Lee, Ran Wei, Jihua Zhang, and Mohamed Elkabbash, all current and former members of the Guo Lab, and Ye Wang, Wenchi Kong, Sandeep Kumar Chamoli, Tao Huang, and Weili Yu, all of the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics, and Physics in China.
The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Army Research Office, and the National Science Foundation supported this research.
See the full article here .
Comments are invited and will be appreciated, especially if the reader finds any errors which I can correct. Use “Reply”.
five-ways-keep-your-child-safe-school-shootings
Please help promote STEM in your local schools.
 University of Rochester campus
University of Rochester campus
The University of Rochester is a private research university in Rochester, New York. The university grants undergraduate and graduate degrees, including doctoral and professional degrees.
The University of Rochester enrolls approximately 6,800 undergraduates and 5,000 graduate students. Its 158 buildings house over 200 academic majors. According to the National Science Foundation , The University of Rochester spent $370 million on research and development in 2018, ranking it 68th in the nation. The University of Rochester is the 7th largest employer in the Finger lakes region of New York.
The College of Arts, Sciences, and Engineering is home to departments and divisions of note. The Institute of Optics was founded in 1929 through a grant from Eastman Kodak and Bausch and Lomb as the first educational program in the US devoted exclusively to Optics and awards approximately half of all Optics degrees nationwide and is widely regarded as the premier Optics program in the nation and among the best in the world.
The Departments of Political Science and Economics have made a significant and consistent impact on positivist social science since the 1960s and historically rank in the top 5 in their fields. The Department of Chemistry is noted for its contributions to synthetic Organic Chemistry, including the first lab-based synthesis of morphine. The Rossell Hope Robbins Library serves as The University of Rochester’s resource for Old and Middle English texts and expertise. The university is also home to Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics, a Department of Energy supported national laboratory.
 The University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.
The University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics.
The University of Rochester’s Eastman School of Music ranks first among undergraduate music schools in the U.S. The Sibley Music Library at Eastman is the largest academic music library in North America and holds the third largest collection in the United States.
In its history The University of Rochester alumni and faculty have earned 13 Nobel Prizes; 13 Pulitzer Prizes; 45 Grammy Awards; 20 Guggenheim Awards; 5 National Academy of Sciences; 4 National Academy of Engineering; 3 Rhodes Scholarships; 3 National Academy of Inventors; and 1 National Academy of Inventors Hall of Fame.
History
Early history
The University of Rochester traces its origins to The First Baptist Church of Hamilton (New York) which was founded in 1796. The church established the Baptist Education Society of the State of New York later renamed the Hamilton Literary and Theological Institution in 1817. This institution gave birth to both Colgate University and the University of Rochester. Its function was to train clergy in the Baptist tradition. When it aspired to grant higher degrees it created a collegiate division separate from the theological division.
The collegiate division was granted a charter by the State of New York in 1846 after which its name was changed to Madison University. John Wilder and the Baptist Education Society urged that the new university be moved to Rochester, New York. However, legal action prevented the move. In response, dissenting faculty, students, and trustees defected and departed for Rochester, where they sought a new charter for a new university.
Madison University was eventually renamed as Colgate University.
Founding
Asahel C. Kendrick- professor of Greek- was among the faculty that departed Madison University for The University of Rochester. Kendrick served as acting president while a national search was conducted. He reprised this role until 1853 when Martin Brewer Anderson of the Newton Theological Seminary in Massachusetts was selected to fill the inaugural posting.
The University of Rochester’s new charter was awarded by the Regents of the State of New York on January 31, 1850. The charter stipulated that The University of Rochester have $100,000 in endowment within five years upon which the charter would be reaffirmed. An initial gift of $10,000 was pledged by John Wilder which helped catalyze significant gifts from individuals and institutions.
Classes began that November with approximately 60 students enrolled including 28 transfers from Madison. From 1850 to 1862 the university was housed in the old United States Hotel in downtown Rochester on Buffalo Street near Elizabeth Street- today West Main Street near the I-490 overpass. On a February 1851 visit Ralph Waldo Emerson said of the university:
“They had bought a hotel, once a railroad terminus depot, for $8,500, turned the dining room into a chapel by putting up a pulpit on one side, made the barroom into a Pythologian Society’s Hall, & the chambers into Recitation rooms, Libraries, & professors’ apartments, all for $700 a year. They had brought an omnibus load of professors down from Madison bag and baggage… called in a painter and sent him up the ladder to paint the title “University of Rochester” on the wall, and they had runners on the road to catch students. And they are confident of graduating a class of ten by the time green peas are ripe.”
For the next 10 years The University of Rochester expanded its scope and secured its future through an expanding endowment; student body; and faculty. In parallel a gift of 8 acres of farmland from local businessman and Congressman Azariah Boody secured the first campus of The University of Rochester upon which Anderson Hall was constructed and dedicated in 1862. Over the next sixty years this Prince Street Campus grew by a further 17 acres and was developed to include fraternity houses; dormitories; and academic buildings including Anderson Hall; Sibley Library; Eastman and Carnegie Laboratories the Memorial Art Gallery and Cutler Union.
Twentieth century
Coeducation
The first female students were admitted in 1900- the result of an effort led by Susan B. Anthony and Helen Barrett Montgomery. During the 1890s a number of women took classes and labs at The University of Rochester as “visitors” but were not officially enrolled nor were their records included in the college register. President David Jayne Hill allowed the first woman- Helen E. Wilkinson- to enroll as a normal student although she was not allowed to matriculate or to pursue a degree. Thirty-three women enrolled among the first class in 1900 and Ella S. Wilcoxen was the first to receive a degree in 1901. The first female member of the faculty was Elizabeth Denio who retired as Professor Emeritus in 1917. Male students moved to River Campus upon its completion in 1930 while the female students remained on the Prince Street campus until 1955.
Expansion
Major growth occurred under the leadership of Benjamin Rush Rhees over his 1900-1935 tenure. During this period George Eastman became a major donor giving more than $50 million to the university during his life. Under the patronage of Eastman the Eastman School of Music was created in 1921. In 1925 at the behest of the General Education Board and with significant support for John D. Rockefeller George Eastman and Henry A. Strong’s family medical and dental schools were created. The university award its first Ph.D that same year.
During World War II The University of Rochester was one of 131 colleges and universities nationally that took part in the V-12 Navy College Training Program which offered students a path to a Navy commission. In 1942, The University of Rochester was invited to join the Association of American Universities as an affiliate member and it was made a full member by 1944. Between 1946 and 1947 in infamous uranium experiments researchers at the university injected uranium-234 and uranium-235 into six people to study how much uranium their kidneys could tolerate before becoming damaged.
In 1955 the separate colleges for men and women were merged into The College on the River Campus. In 1958 three new schools were created in engineering, business administration and education. The Graduate School of Management was named after William E. Simon- former Secretary of the Treasury in 1986. He committed significant funds to the school because of his belief in the school’s free market philosophy and grounding in economic analysis.
Financial decline and name change controversy
Following the princely gifts given throughout his life George Eastman left the entirety of his estate to The University of Rochester after his death by suicide. The total of these gifts surpassed $100 million before inflation and as such The University of Rochester enjoyed a privileged position amongst the most well endowed universities. During the expansion years between 1936 and 1976 The University of Rochester’s financial position ranked third, near Harvard University’s endowment and the University of Texas System’s Permanent University Fund . Due to a decline in the value of large investments and a lack of portfolio diversity The University of Rochester ‘s place dropped to the top 25 by the end of the 1980s. At the same time the preeminence of the city of Rochester’s major employers began to decline.
In response The University of Rochester commissioned a study to determine if the name of the institution should be changed to “Eastman University” or “Eastman Rochester University”. The study concluded a name change could be beneficial because the use of a place name in the title led respondents to incorrectly believe it was a public university, and because the name “Rochester” connoted a “cold and distant outpost.” Reports of the latter conclusion led to controversy and criticism in the Rochester community. Ultimately, the name “The University of Rochester” was retained.
Renaissance Plan
In 1995 The University of Rochester president Thomas H. Jackson announced the launch of a “Renaissance Plan” for The University of Rochester that reduced enrollment from 4,500 to 3,600 creating a more selective admissions process. The plan also revised the undergraduate curriculum significantly creating the current system with only one required course and only a few distribution requirements known as clusters. Part of this plan called for the end of graduate doctoral studies in Chemical Engineering; comparative literature; linguistics; and Mathematics, the last of which was met by national outcry. The plan was largely scrapped and Mathematics exists as a graduate course of study to this day.
Twenty-first century
Meliora Challenge
Shortly after taking office university president Joel Seligman commenced the private phase of the “Meliora Challenge”- a $1.2 billion capital campaign- in 2005. The campaign reached its goal in 2015- a year before the campaign was slated to conclude. In 2016, The University of Rochester announced the Meliora Challenge had exceeded its goal and surpassed $1.36 billion. These funds were allocated to support over 100 new endowed faculty positions and nearly 400 new scholarships.
The Mangelsdorf Years
On December 17, 2018 The University of Rochester announced that Sarah C. Mangelsdorf would succeed Richard Feldman as President of the University. Her term started in July 2019 with a formal inauguration following in October during Meliora Weekend. Mangelsdorf is the first woman to serve as President of the University and the first person with a degree in psychology to be appointed to Rochester’s highest office.
In 2019 students from China mobilized by the Chinese Students and Scholars Association (CSSA) defaced murals in the University’s access tunnels which had expressed support for the 2019 Hong Kong Protests, condemned the oppression of the Uighurs, and advocated for Taiwanese independence. The act was widely seen as a continuation of overseas censorship of Chinese issues. In response a large group of students recreated the original murals. There have also been calls for Chinese government run CSSA to be banned from campus.
Research
The University of Rochester is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among “R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity”.
The University of Rochester had a research expenditure of $370 million in 2018.
In 2008 The University of Rochester ranked 44th nationally in research spending but this ranking has declined gradually to 68 in 2018.
Some of the major research centers include the Laboratory for Laser Energetics, a laser-based nuclear fusion facility, and the extensive research facilities at the University of Rochester Medical Center.
Recently The University of Rochester has also engaged in a series of new initiatives to expand its programs in Biomedical Engineering and Optics including the construction of the new $37 million Robert B. Goergen Hall for Biomedical Engineering and Optics on the River Campus.
Other new research initiatives include a cancer stem cell program and a Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute. The University of Rochester also has the ninth highest technology revenue among U.S. higher education institutions with $46 million being paid for commercial rights to university technology and research in 2009. Notable patents include Zoloft and Gardasil. WeBWorK, a web-based system for checking homework and providing immediate feedback for students was developed by The University of Rochester professors Gage and Pizer. The system is now in use at over 800 universities and colleges as well as several secondary and primary schools. The University of Rochester scientists work in diverse areas. For example, physicists developed a technique for etching metal surfaces such as platinum; titanium; and brass with powerful lasers enabling self-cleaning surfaces that repel water droplets and will not rust if tilted at a 4 degree angle; and medical researchers are exploring how brains rid themselves of toxic waste during sleep.

