From The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
And

5.23.24
Francis Reddy
francis.j.reddy@nasa.gov
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
301-286-1940
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Using observations by NASA’s TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) and many other facilities, two international teams of astronomers have discovered a planet between the sizes of Earth and Venus only 40 light-years away. Multiple factors make it a candidate well-suited for further study using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.

Gliese 12 b, which orbits a cool red dwarf star located just 40 light-years away, promises to tell astronomers more about how planets close to their stars retain or lose their atmospheres. In this artist’s concept, Gliese 12 b is shown retaining a thin atmosphere. Credit: R. Hurt (Caltech-IPAC)/NASA/JPL-Caltech
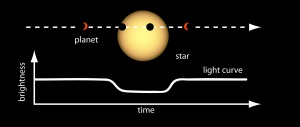
TESS stares at a large swath of the sky for about a month at a time, tracking the brightness changes of tens of thousands of stars at intervals ranging from 20 seconds to 30 minutes. Capturing transits — brief, regular dimmings of stars caused by the passage of orbiting worlds — is one of the mission’s primary goals.
“We’ve found the nearest, transiting, temperate, Earth-size world located to date,” said Masayuki Kuzuhara, a project assistant professor at the Astrobiology Center
in Tokyo, who co-led one research team with Akihiko Fukui, a project assistant professor at the University of Tokyo. “Although we don’t yet know whether it possesses an atmosphere, we’ve been thinking of it as an exo-Venus, with similar size and energy received from its star as our planetary neighbor in the solar system.”
The host star, called Gliese 12, is a cool red dwarf located almost 40 light-years away in the constellation Pisces. The star is only about 27% of the Sun’s size, with about 60% of the Sun’s surface temperature. The newly discovered world, named Gliese 12 b, orbits every 12.8 days and is Earth’s size or slightly smaller — comparable to Venus. Assuming it has no atmosphere, the planet has a surface temperature estimated at around 107 degrees Fahrenheit (42 degrees Celsius).
Astronomers say that the diminutive sizes and masses of red dwarf stars make them ideal for finding Earth-size planets. A smaller star means greater dimming for each transit, and a lower mass means an orbiting planet can produce a greater wobble, known as “reflex motion,” of the star. These effects make smaller planets easier to detect.

Gliese 12 b’s estimated size may be as large as Earth or slightly smaller — comparable to Venus in our solar system. This artist’s concept compares Earth with different possible Gliese 12 b interpretations, from one with no atmosphere to one with a thick Venus-like one. Follow-up observations with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope could help determine just how much atmosphere the planet retains as well as its composition. Credit: R. Hurt (Caltech-IPAC)/NASA/JPL-Caltech
The lower luminosities of red dwarf stars also means their habitable zones — the range of orbital distances where liquid water could exist on a planet’s surface — lie closer to them. This makes it easier to detect transiting planets within habitable zones around red dwarfs than those around stars emitting more energy.
The distance separating Gliese 12 and the new planet is just 7% of the distance between Earth and the Sun. The planet receives 1.6 times more energy from its star as Earth does from the Sun and about 85% of what Venus experiences.
“Gliese 12 b represents one of the best targets to study whether Earth-size planets orbiting cool stars can retain their atmospheres, a crucial step to advance our understanding of habitability on planets across our galaxy,” said Shishir Dholakia, a doctoral student at the Centre for Astrophysics at the University of Southern Queensland in Australia. He co-led a different research team with Larissa Palethorpe, a doctoral student at the University of Edinburgh and University College London.
Both teams suggest that studying Gliese 12 b may help unlock some aspects of our own solar system’s evolution.
“It is thought that Earth’s and Venus’s first atmospheres were stripped away and then replenished by volcanic outgassing and bombardments from residual material in the solar system,” Palethorpe explained. “The Earth is habitable, but Venus is not due to its complete loss of water. Because Gliese 12 b is between Earth and Venus in temperature, its atmosphere could teach us a lot about the habitability pathways planets take as they develop.”
One important factor in retaining an atmosphere is the storminess of its star. Red dwarfs tend to be magnetically active, resulting in frequent, powerful X-ray flares. However, analyses by both teams conclude that Gliese 12 shows no signs of extreme behavior.
A paper led by Kuzuhara and Fukui was published May 23 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. The Dholakia and Palethorpe findings were published in MNRAS on the same day.
During a transit, the host star’s light passes through any atmosphere.
Different gas molecules absorb different colors, so the transit provides a set of chemical fingerprints that can be detected by telescopes like Webb.
“We know of only a handful of temperate planets similar to Earth that are both close enough to us and meet other criteria needed for this kind of study, called transmission spectroscopy, using current facilities,” said Michael McElwain, a research astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and a co-author of the Kuzuhara and Fukui paper. “To better understand the diversity of atmospheres and evolutionary outcomes for these planets, we need more examples like Gliese 12 b.”
TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission managed by NASA Goddard and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Additional partners include Northrop Grumman, based in Falls Church, Virginia; NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley; the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian in Cambridge, Massachusetts; MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory; and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. More than a dozen universities, research institutes, and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission.
See the full article here.
Comments are invited and will be appreciated, especially if the reader finds any errors which I can correct.

five-ways-keep-your-child-safe-school-shootings
Please help promote STEM in your local schools.
National Aeronautics Space Agency/Massachusetts Institute of Technology TESS

TESS [Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite] replaced the Kepler Space Telescope in search for exoplanets.

TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.

The Massachusetts Institute of Technology

The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Additional partners include Northrop Grumman, based in Falls Church, Virginia; NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley; the Center for Astrophysics – Harvard and Smithsonian; MIT Lincoln Laboratory; and the NASA Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore.
The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD is home to the nation’s largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
Named for American rocketry pioneer Dr. Robert H. Goddard, the center was established in 1959 as NASA’s first space flight complex. Goddard and its several facilities are critical in carrying out NASA’s missions of space exploration and scientific discovery.
GSFC also operates two spaceflight tracking and data acquisition networks (the NASA Deep Space Network and the Near Earth Network); develops and maintains advanced space and Earth science data information systems, and develops satellite systems for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
GSFC manages operations for many NASA and international missions including the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope; the Explorers Program; the Discovery Program; the Earth Observing System; INTEGRAL; MAVEN; OSIRIS-REx; the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory ; the Solar Dynamics Observatory; Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System ; Fermi; and Swift. Past missions managed by GSFC include the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE), Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, SMM, COBE, IUE, and ROSAT. Typically, unmanned Earth observation missions and observatories in Earth orbit are managed by GSFC, while unmanned planetary missions are managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California.
Goddard is one of four centers built by NASA since its founding on July 29, 1958. It is NASA’s first, and oldest, space center. Its original charter was to perform five major functions on behalf of NASA: technology development and fabrication; planning; scientific research; technical operations; and project management. The center is organized into several directorates, each charged with one of these key functions.
Until May 1, 1959, NASA’s presence in Greenbelt, MD was known as the Beltsville Space Center. It was then renamed the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), after Robert H. Goddard. Its first 157 employees transferred from the United States Navy’s Project Vanguard missile program, but continued their work at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C., while the center was under construction.
Goddard Space Flight Center contributed to Project Mercury, America’s first manned space flight program. The Center assumed a lead role for the project in its early days and managed the first 250 employees involved in the effort, who were stationed at Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. However, the size and scope of Project Mercury soon prompted NASA to build a new Manned Spacecraft Center, now the Johnson Space Center, in Houston, Texas. Project Mercury’s personnel and activities were transferred there in 1961.
The Goddard network tracked many early manned and unmanned spacecraft.
Goddard Space Flight Center remained involved in the manned space flight program, providing computer support and radar tracking of flights through a worldwide network of ground stations called the Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network (STDN). However, the Center focused primarily on designing unmanned satellites and spacecraft for scientific research missions. Goddard pioneered several fields of spacecraft development, including modular spacecraft design, which reduced costs and made it possible to repair satellites in orbit. Goddard’s Solar Max satellite, launched in 1980, was repaired by astronauts on the Space Shuttle Challenger in 1984. The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, remains in service and continues to grow in capability thanks to its modular design and multiple servicing missions by the Space Shuttle.
Today, the center remains involved in each of NASA’s key programs. Goddard has developed more instruments for planetary exploration than any other organization, among them scientific instruments sent to every planet in the Solar System. The center’s contribution to the Earth Science Enterprise includes several spacecraft in the Earth Observing System fleet as well as EOSDIS, a science data collection, processing, and distribution system. For the manned space flight program, Goddard develops tools for use by astronauts during extra-vehicular activity, and operates the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, a spacecraft designed to study the Moon in preparation for future manned exploration.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation’s civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research.

President Dwight D. Eisenhower established the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1958 with a distinctly civilian (rather than military) orientation encouraging peaceful applications in space science. The National Aeronautics and Space Act was passed on July 29, 1958, disestablishing NASA’s predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). The new agency became operational on October 1, 1958.
Since that time, most U.S. space exploration efforts have been led by NASA, including the Apollo moon-landing missions, the Skylab space station, and later the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA is supporting the International Space Station and is overseeing the development of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and Commercial Crew vehicles. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program (LSP) which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for unmanned NASA launches. Most recently, NASA announced a new Space Launch System that it said would take the agency’s astronauts farther into space than ever before and lay the cornerstone for future human space exploration efforts by the U.S.
NASA science is focused on better understanding Earth through the Earth Observing System, advancing heliophysics through the efforts of the Science Mission Directorate’s Heliophysics Research Program, exploring bodies throughout the Solar System with advanced robotic missions such as New Horizons, and researching astrophysics topics, such as the Big Bang, through the Great Observatories [Hubble, Chandra, Spitzer, and associated programs.] NASA shares data with various national and international organizations such as from the [JAXA]Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite.






