From The School of Engineering
At
3.25.24
Andrew Myers
Stanford materials engineers have 3D printed tens of thousands of hard-to-manufacture nanoparticles long predicted to yield promising new materials that change form in an instant.
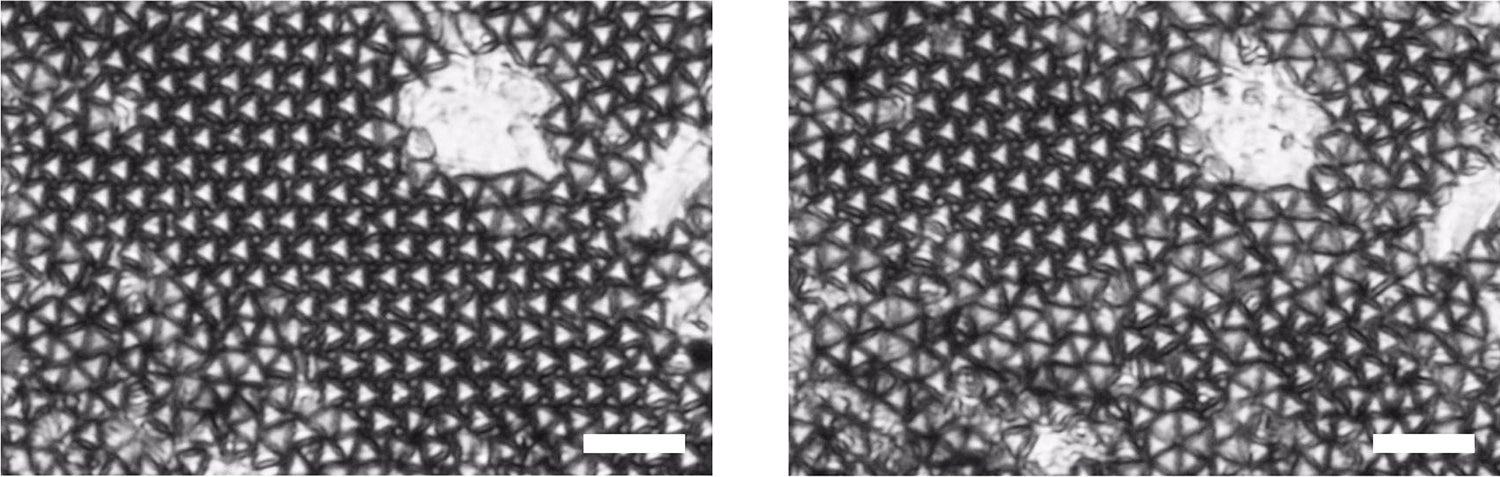
Optical images of truncated tetrahedrons forming two large hexagonal grains at an anti-phase boundary (left), and transforming into a quasi-diamond phase that initiated at the anti-phase boundary (right). Scale bars are 25 um. (Image credit: David Doan & John Kulikowski)
In nanomaterials, shape is destiny. That is, the geometry of the particle in the material defines the physical characteristics of the resulting material.
“A crystal made of nano-ball bearings will arrange themselves differently than a crystal made of nano-dice and these arrangements will produce very different physical properties,” said Wendy Gu, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Stanford University, introducing her latest paper which appears in the journal Nature Communications. “We’ve used a 3D nanoprinting technique to produce one of the most promising shapes known – Archimedean truncated tetrahedrons. They are micron-scale tetrahedrons with the tips lopped off.”
In the paper, Gu and her co-authors describe how they nanoprinted tens of thousands of these challenging nanoparticles, stirred them into a solution, and then watched as they self-assembled into various promising crystal structures. More critically, these materials can shift between states in minutes simply by rearranging the particles into new geometric patterns.
This ability to change “phases,” as materials engineers refer to the shapeshifting quality, is similar to the atomic rearrangement that turns iron into tempered steel, or in materials that allow computers to store terabytes of valuable data in digital form.
“If we can learn to control these phase shifts in materials made of these Archimedean truncated tetrahedrons it could lead in many promising engineering directions,” she said.
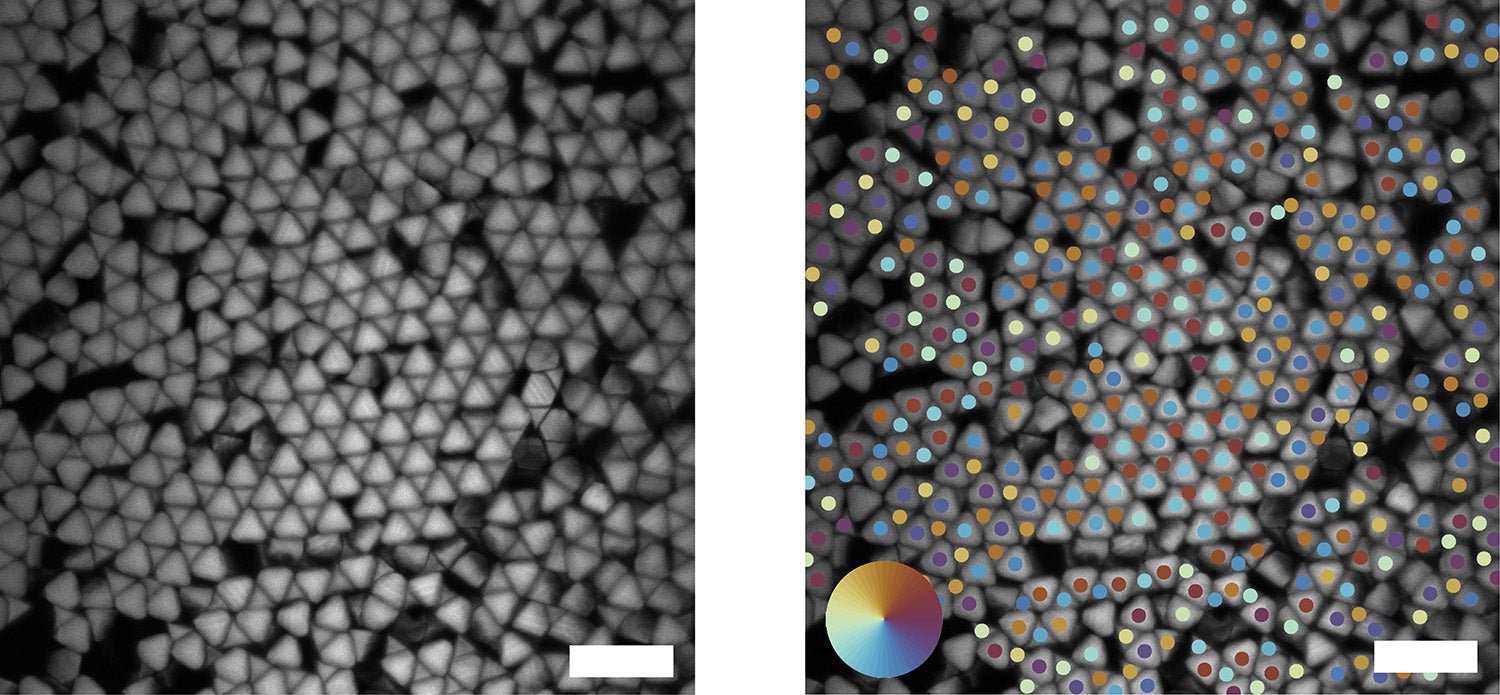
Confocal images of truncated tetrahedrons forming several quasi-diamond grains (left). Bond order analysis shows different quasi-diamond grains through alternating colors (right). Neighboring tetrahedrons that have alternating colors (i.e. blue and red/brown, or dark blue and yellow) indicate that they have the same grain orientation. Scale bars are 20 um. (Image credit: David Doan & John Kulikowski)
Elusive prey
Archimedean truncated tetrahedrons (ATTs) have long been theorized to be among the most desirable of geometries for producing materials that can easily change phase, but until recently were challenging to fabricate – predicted in computer simulations yet difficult to reproduce in the real world.
Gu is quick to point out that her team is not the first to produce nanoscale Archimedean truncated tetrahedrons in quantity, but they are among the first, if not the first, to use 3D nanoprinting to do it.
“With 3D nanoprinting, we can make almost any shape we want. We can control the particle shape very carefully,” Gu explained. “This particular shape has been predicted by simulations to form very interesting structures. When you can pack them together in various ways they produce valuable physical properties.”
ATTs form at least two highly desirable geometric structures. The first is a hexagonal pattern in which the tetrahedrons rest flat on the substrate with their truncated tips pointing upward like a nanoscale mountain range. The second is perhaps even more promising, Gu said. It is a crystalline quasi-diamond structure in which the tetrahedrons alternate in upward- and downward-facing orientations, like eggs resting in an egg carton. The diamond arrangement is considered a “Holy Grail” in the photonics community and could lead in many new and interesting scientific directions.
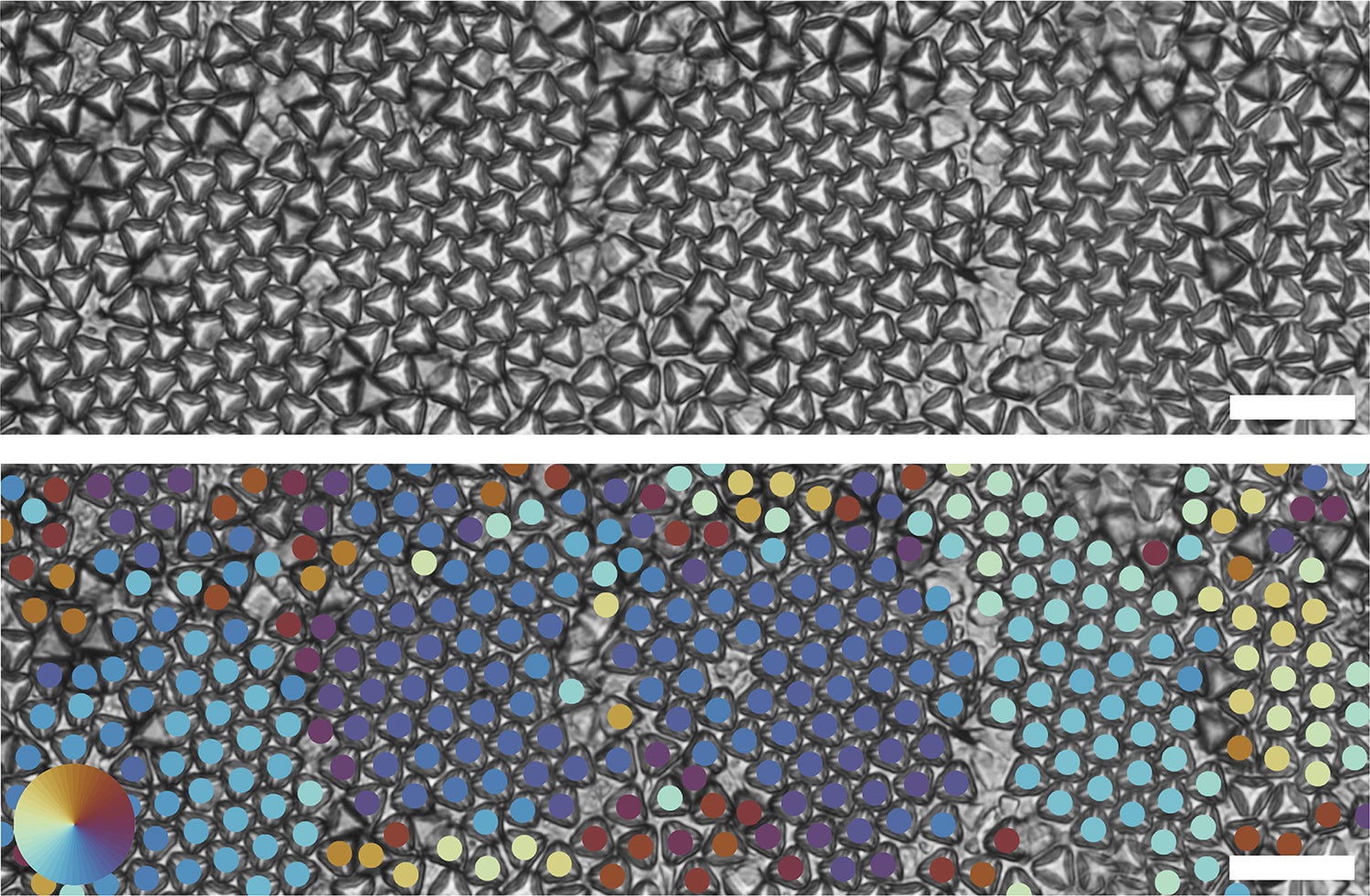
Optical images of truncated tetrahedrons forming multiple hexagonal grains (top). Bond order analysis shows different hexagonal grains through different colors (bottom). Neighboring tetrahedrons that have the same color indicate that they have the same grain orientation. Scale bar is 20 um. (Image credit: David Doan & John Kulikowski)
Most importantly, however, when properly engineered, future materials made of 3D printed particles can be rearranged rapidly, switching easily back and forth between phases with the application of a magnetic field, electric current, heat, or other engineering method.
Gu said she can imagine coatings for solar panels that change throughout the day to maximize energy efficiency, new-age hydrophobic films for airplane wings and windows that mean they never fog or ice up, or new types of computer memory. The list goes on and on.
“Right now, we’re working on making these particles magnetic to control how they behave,” Gu said of her latest research already underway using Archimedean truncated tetrahedron nanoparticles in new ways. “The possibilities are only beginning to be explored.”
See the full article here .
Comments are invited and will be appreciated, especially if the reader finds any errors which I can correct.
five-ways-keep-your-child-safe-school-shootings
Please help promote STEM in your local schools.
The Stanford University School of Engineering has been at the forefront of innovation for nearly a century, creating pivotal technologies that have transformed the worlds of information technology, communications, health care, energy, business and beyond.
The school’s faculty, students and alumni have established thousands of companies and laid the technological and business foundations for Silicon Valley. Today, the school educates leaders who will make an impact on global problems and seeks to define what the future of engineering will look like.
Mission
Our mission is to seek solutions to important global problems and educate leaders who will make the world a better place by using the power of engineering principles, techniques and systems. We believe it is essential to educate engineers who possess not only deep technical excellence, but the creativity, cultural awareness and entrepreneurial skills that come from exposure to the liberal arts, business, medicine and other disciplines that are an integral part of the Stanford experience.
Our key goals are to:
Conduct curiosity-driven and problem-driven research that generates new knowledge and produces discoveries that provide the foundations for future engineered systems
Deliver world-class, research-based education to students and broad-based training to leaders in academia, industry and society
Drive technology transfer to Silicon Valley and beyond with deeply and broadly educated people and transformative ideas that will improve our society and our world.
The Future of Engineering
The engineering school of the future will look very different from what it looks like today. So, in 2015, we brought together a wide range of stakeholders, including mid-career faculty, students and staff, to address two fundamental questions: In what areas can the School of Engineering make significant world‐changing impact, and how should the school be configured to address the major opportunities and challenges of the future?
One key output of the process is a set of 10 broad, aspirational questions on areas where the School of Engineering would like to have an impact in 20 years. The committee also returned with a series of recommendations that outlined actions across three key areas — research, education and culture — where the school can deploy resources and create the conditions for The Stanford University College of Engineering to have significant impact on those challenges.
From Stanford University

Leland and Jane Stanford founded Stanford University to “promote the public welfare by exercising an influence on behalf of humanity and civilization.” Stanford opened its doors in 1891, and more than a century later, it remains dedicated to finding solutions to the great challenges of the day and to preparing our students for leadership in today’s complex world. Stanford, is an American private research university located in Stanford, California on an 8,180-acre (3,310 ha) campus near Palo Alto. Since 1952, more than 54 Stanford faculty, staff, and alumni have won the Nobel Prize, including 19 current faculty members.
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university located in Stanford, California. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Stanford is consistently ranked as among the most prestigious and top universities in the world by major education publications. It is also one of the top fundraising institutions in the country, becoming the first school to raise more than a billion dollars in a year.
Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost Frederick Terman supported faculty and graduates’ entrepreneurialism to build self-sufficient local industry in what would later be known as Silicon Valley.
The university is organized around seven schools: three schools consisting of 40 academic departments at the undergraduate level as well as four professional schools that focus on graduate programs in law, medicine, education, and business. All schools are on the same campus. Students compete in 36 varsity sports, and the university is one of two private institutions in the Division I FBS Pac-12 Conference. It has gained many NCAA team championships, and Stanford has won the NACDA Directors’ Cup for many years. In addition, Stanford students and alumni have won many Olympic medals including many gold medals.
Nobel laureates, Turing Award laureates, and Fields Medalists have been affiliated with Stanford as students, alumni, faculty, or staff. In addition, Stanford is particularly noted for its entrepreneurship and is one of the most successful universities in attracting funding for start-ups. Stanford alumni have founded numerous companies. Stanford is the alma mater of presidents of the United States, a number of living billionaires, and a number of astronauts. It is also one of the leading producers of Fulbright Scholars, Marshall Scholars, Rhodes Scholars, and members of the United States Congress.
Stanford University was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford, dedicated to Leland Stanford Jr, their only child. The institution opened in 1891 on Stanford’s previous Palo Alto farm.
Jane and Leland Stanford modeled their university after the great eastern universities, most specifically Cornell University. Stanford opened being called the “Cornell of the West” in 1891 due to faculty being former Cornell affiliates (either professors, alumni, or both) including its first president, David Starr Jordan, and second president, John Casper Branner. Both Cornell and Stanford were among the first to have higher education be accessible, nonsectarian, and open to women as well as to men. Cornell is credited as one of the first American universities to adopt this radical departure from traditional education, and Stanford became an early adopter as well.
Despite being impacted by earthquakes in both 1906 and 1989, the campus was rebuilt each time. In 1919, The Hoover Institution on War, Revolution and Peace was started by Herbert Hoover to preserve artifacts related to World War I. The Stanford Medical Center, completed in 1959, is a teaching hospital with over 800 beds. The DOE’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center), established in 1962, performs research in particle physics.

Land
Most of Stanford is on an 8,180-acre (12.8 sq mi; 33.1 km^2) campus, one of the largest in the United States. It is located on the San Francisco Peninsula, in the northwest part of the Santa Clara Valley (Silicon Valley) approximately 37 miles (60 km) southeast of San Francisco and approximately 20 miles (30 km) northwest of San Jose. In 2008, 60% of this land remained undeveloped.
Stanford’s main campus includes a census-designated place within unincorporated Santa Clara County, although some of the university land (such as the Stanford Shopping Center and the Stanford Research Park) is within the city limits of Palo Alto. The campus also includes much land in unincorporated San Mateo County (including the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the Jasper Ridge Biological Preserve), as well as in the city limits of Menlo Park (Stanford Hills neighborhood), Woodside, and Portola Valley.
Non-central campus
Stanford currently operates in various locations outside of its central campus.
On the founding grant:
Jasper Ridge Biological Preserve is a 1,200-acre (490 ha) natural reserve south of the central campus owned by the university and used by wildlife biologists for research.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is a facility west of the central campus operated by the university for the Department of Energy. It contains the longest linear particle accelerator in the world, 2 miles (3.2 km) on 426 acres (172 ha) of land. Golf course and a seasonal lake: The university also has its own golf course and a seasonal lake (Lake Lagunita, actually an irrigation reservoir), both home to the vulnerable California tiger salamander. As of 2012 Lake Lagunita was often dry and the university had no plans to artificially fill it.
Off the founding grant:
Hopkins Marine Station, in Pacific Grove, California, is a marine biology research center owned by the university since 1892., in Pacific Grove, California, is a marine biology research center owned by the university since 1892.
Study abroad locations: unlike typical study abroad programs, Stanford itself operates in several locations around the world; thus, each location has Stanford faculty-in-residence and staff in addition to students, creating a “mini-Stanford”.
Redwood City campus for many of the university’s administrative offices located in Redwood City, California, a few miles north of the main campus. In 2005, the university purchased a small, 35-acre (14 ha) campus in Midpoint Technology Park intended for staff offices; development was delayed by The Great Recession. In 2015 the university announced a development plan and the Redwood City campus opened in March 2019.
The Bass Center in Washington, DC provides a base, including housing, for the Stanford in Washington program for undergraduates. It includes a small art gallery open to the public.
China: Stanford Center at Peking University, housed in the Lee Jung Sen Building, is a small center for researchers and students in collaboration with Beijing University [北京大学](CN) (Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at Peking University (CN) (KIAA-PKU).
Administration and organization
Stanford is a private, non-profit university that is administered as a corporate trust governed by a privately appointed board of trustees with a maximum membership of 38. Trustees serve five-year terms (not more than two consecutive terms) and meet five times annually. A new trustee is chosen by the current trustees by ballot. The Stanford trustees also oversee the Stanford Research Park, the Stanford Shopping Center, the Cantor Center for Visual Arts, Stanford University Medical Center, and many associated medical facilities (including the Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital).
The board appoints a president to serve as the chief executive officer of the university, to prescribe the duties of professors and course of study, to manage financial and business affairs, and to appoint nine vice presidents. The provost is the chief academic and budget officer, to whom the deans of each of the seven schools report.
As of 2018, the university was organized into seven academic schools. The schools of Humanities and Sciences (27 departments), Engineering (nine departments), and Earth, Energy & Environmental Sciences (four departments) have both graduate and undergraduate programs while the Schools of Law, Medicine, Education and Business have graduate programs only. The powers and authority of the faculty are vested in the Academic Council, which is made up of tenure and non-tenure line faculty, research faculty, senior fellows in some policy centers and institutes, the president of the university, and some other academic administrators, but most matters are handled by the Faculty Senate, made up of 55 elected representatives of the faculty.
The Associated Students of Stanford University (ASSU) is the student government for Stanford and all registered students are members. Its elected leadership consists of the Undergraduate Senate elected by the undergraduate students, the Graduate Student Council elected by the graduate students, and the President and Vice President elected as a ticket by the entire student body.
Stanford is the beneficiary of a special clause in the California Constitution, which explicitly exempts Stanford property from taxation so long as the property is used for educational purposes.
Endowment and donations
In the NACUBO-TIAA survey of colleges and universities in the United States and Canada, only Harvard University, the University of Texas System, and Yale University had larger endowments than Stanford.
In 2006, President John L. Hennessy launched a five-year campaign called the “Stanford Challenge”, which reached its $4.3 billion fundraising goal in 2009, two years ahead of time, but continued fundraising for the duration of the campaign. It concluded on December 31, 2011, having raised a total of $6.23 billion and breaking the previous campaign fundraising record of $3.88 billion held by Yale. Specifically, the campaign raised $253.7 million for undergraduate financial aid, as well as $2.33 billion for its initiative in “Seeking Solutions” to global problems, $1.61 billion for “Educating Leaders” by improving K-12 education, and $2.11 billion for “Foundation of Excellence” aimed at providing academic support for Stanford students and faculty. Funds supported a large number of new fellowships for graduate students, a number of newly endowed chairs for faculty, and some new or renovated buildings. The new funding also enabled the construction of a facility for stem cell research; a new campus for the business school; an expansion of the law school; a new Engineering Quad; a new art and art history building; an on-campus concert hall; a new art museum; and a planned expansion of the medical school, among other things. In 2012, the university raised $1.035 billion, becoming the first school to raise more than a billion dollars in a year.
Research centers and institutes
DOE’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Stanford Research Institute, a center of innovation to support economic development in the region.
Hoover Institution, a conservative American public policy institution and research institution that promotes personal and economic liberty, free enterprise, and limited government.
Hasso Plattner Institute of Design, a multidisciplinary design school in cooperation with the Hasso Plattner Institute of University of Potsdam [Universität Potsdam](DE) that integrates product design, engineering, and business management education).
Martin Luther King Jr. Research and Education Institute, which grew out of and still contains the Martin Luther King Jr. Papers Project.
John S. Knight Fellowship for Professional Journalists
Center for Ocean Solutions
Together with University of California-Berkeley and University of California-San Francisco, Stanford is part of the Biohub, a new medical science research center founded in 2016 by a $600 million commitment from Facebook CEO and founder Mark Zuckerberg and pediatrician Priscilla Chan.
Discoveries and innovation
Natural sciences
Biological synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) – Arthur Kornberg synthesized DNA material and won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959 for his work at Stanford.
First Transgenic organism – Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer were the first scientists to transplant genes from one living organism to another, a fundamental discovery for genetic engineering. Thousands of products have been developed on the basis of their work, including human growth hormone and hepatitis B vaccine.
Laser – Arthur Leonard Schawlow shared the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physics with Nicolaas Bloembergen and Kai Siegbahn for his work on lasers.
Nuclear magnetic resonance – Felix Bloch developed new methods for nuclear magnetic precision measurements, which are the underlying principles of the MRI.
Computer and applied sciences
ARPANET – Stanford Research Institute, formerly part of Stanford but on a separate campus, was the site of one of the four original ARPANET nodes.
Internet—Stanford was the site where the original design of the Internet was undertaken. Vint Cerf led a research group to elaborate the design of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP/IP) that he originally co-created with Robert E. Kahn (Bob Kahn) in 1973 and which formed the basis for the architecture of the Internet.
Frequency modulation synthesis – John Chowning of the Music department invented the FM music synthesis algorithm in 1967, and Stanford later licensed it to Yamaha Corporation.
Google – Google began in January 1996 as a research project by Larry Page and Sergey Brin when they were both PhD students at Stanford. They were working on the Stanford Digital Library Project (SDLP). The SDLP’s goal was “to develop the enabling technologies for a single, integrated and universal digital library” and it was funded through the National Science Foundation, among other federal agencies.
Klystron tube – invented by the brothers Russell and Sigurd Varian at Stanford. Their prototype was completed and demonstrated successfully on August 30, 1937. Upon publication in 1939, news of the klystron immediately influenced the work of U.S. and UK researchers working on radar equipment.
RISC – ARPA funded VLSI project of microprocessor design. Stanford and University of California- Berkeley are most associated with the popularization of this concept. The Stanford MIPS would go on to be commercialized as the successful MIPS architecture, while Berkeley RISC gave its name to the entire concept, commercialized as the SPARC. Another success from this era were IBM’s efforts that eventually led to the IBM POWER instruction set architecture, PowerPC, and Power ISA. As these projects matured, a wide variety of similar designs flourished in the late 1980s and especially the early 1990s, representing a major force in the Unix workstation market as well as embedded processors in laser printers, routers and similar products.
SUN workstation – Andy Bechtolsheim designed the SUN workstation for the Stanford University Network communications project as a personal CAD workstation, which led to Sun Microsystems.
Businesses and entrepreneurship
Stanford is one of the most successful universities in creating companies and licensing its inventions to existing companies; it is often held up as a model for technology transfer. Stanford’s Office of Technology Licensing is responsible for commercializing university research, intellectual property, and university-developed projects.
The university is described as having a strong venture culture in which students are encouraged, and often funded, to launch their own companies.
Companies founded by Stanford alumni generate more than $2.7 trillion in annual revenue, equivalent to the 10th-largest economy in the world.
Some companies closely associated with Stanford and their connections include:
Hewlett-Packard, 1939, co-founders William R. Hewlett (B.S, PhD) and David Packard (M.S).
Silicon Graphics, 1981, co-founders James H. Clark (Associate Professor) and several of his grad students.
Sun Microsystems, 1982, co-founders Vinod Khosla (M.B.A), Andy Bechtolsheim (PhD) and Scott McNealy (M.B.A).
Cisco, 1984, founders Leonard Bosack (M.S) and Sandy Lerner (M.S) who were in charge of Stanford Computer Science and Graduate School of Business computer operations groups respectively when the hardware was developed.
Yahoo!, 1994, co-founders Jerry Yang (B.S, M.S) and David Filo (M.S).
Google, 1998, co-founders Larry Page (M.S) and Sergey Brin (M.S).
LinkedIn, 2002, co-founders Reid Hoffman (B.S), Konstantin Guericke (B.S, M.S), Eric Lee (B.S), and Alan Liu (B.S).
Instagram, 2010, co-founders Kevin Systrom (B.S) and Mike Krieger (B.S).
Snapchat, 2011, co-founders Evan Spiegel and Bobby Murphy (B.S).
Coursera, 2012, co-founders Andrew Ng (Associate Professor) and Daphne Koller (Professor, PhD).
Student body
Women comprised 50.4% of undergraduates and 41.5% of graduate students. The freshman retention rate has been 99%.
The relatively low four-year graduation rate is a function of the university’s coterminal degree (or “coterm”) program, which allows students to earn a master’s degree as a 1-to-2-year extension of their undergraduate program.
Fifteen percent of undergraduates have been first-generation students.
Athletics
Stanford had 16 male varsity sports and 20 female varsity sports, 19 club sports and about 27 intramural sports. In 1930, following a unanimous vote by the Executive Committee for the Associated Students, the athletic department adopted the mascot “Indian.” The Indian symbol and name were dropped by President Richard Lyman in 1972, after objections from Native American students and a vote by the student senate. The sports teams are now officially referred to as the “Stanford Cardinal,” referring to the deep red color, not the cardinal bird. Stanford is a member of the Pac-12 Conference in most sports, the Mountain Pacific Sports Federation in several other sports, and the America East Conference in field hockey with the participation in the inter-collegiate NCAA’s Division I FBS.
Its traditional sports rival is the University of California-Berkeley, the neighbor to the north in the East Bay. The winner of the annual “Big Game” between the Cal and Cardinal football teams gains custody of the Stanford Axe.
Stanford has had at least one NCAA team champion every year since the 1976–77 school year and has earned many NCAA national team titles since its establishment, the most among universities, and Stanford has won many individual national championships, the most by any university. Stanford has won the award for the top-ranked Division 1 athletic program—the NACDA Directors’ Cup, formerly known as the Sears Cup—annually for the past twenty-four straight years. Stanford athletes have won medals in every Olympic Games since 1912, winning a large number of Olympic medals in total, many of them gold. In the 2008 Summer Olympics, and 2016 Summer Olympics, Stanford won more Olympic medals than any other university in the United States. Stanford athletes won 16 medals at the 2012 Summer Olympics (12 gold, two silver and two bronze), and 27 medals at the 2016 Summer Olympics.
Traditions
The unofficial motto of Stanford, selected by President Jordan, is Die Luft der Freiheit weht. Translated from the German language, this quotation from Ulrich von Hutten means, “The wind of freedom blows.” The motto was controversial during World War I, when anything in German was suspect; at that time the university disavowed that this motto was official.
Hail, Stanford, Hail! is the Stanford Hymn sometimes sung at ceremonies or adapted by the various University singing groups. It was written in 1892 by mechanical engineering professor Albert W. Smith and his wife, Mary Roberts Smith (in 1896 she earned the first Stanford doctorate in Economics and later became associate professor of Sociology), but was not officially adopted until after a performance on campus in March 1902 by the Mormon Tabernacle Choir.
“Uncommon Man/Uncommon Woman”: Stanford does not award honorary degrees, but in 1953 the degree of “Uncommon Man/Uncommon Woman” was created to recognize individuals who give rare and extraordinary service to the University. Technically, this degree is awarded by the Stanford Associates, a voluntary group that is part of the university’s alumni association. As Stanford’s highest honor, it is not conferred at prescribed intervals, but only when appropriate to recognize extraordinary service. Recipients include Herbert Hoover, Bill Hewlett, Dave Packard, Lucile Packard, and John Gardner.
Big Game events: The events in the week leading up to the Big Game vs. UC- Berkeley, including Gaieties (a musical written, composed, produced, and performed by the students of Ram’s Head Theatrical Society).
“Viennese Ball”: a formal ball with waltzes that was initially started in the 1970s by students returning from the now-closed Stanford in Vienna overseas program. It is now open to all students.
“Full Moon on the Quad”: An annual event at Main Quad, where students gather to kiss one another starting at midnight. Typically organized by the Junior class cabinet, the festivities include live entertainment, such as music and dance performances.
“Band Run”: An annual festivity at the beginning of the school year, where the band picks up freshmen from dorms across campus while stopping to perform at each location, culminating in a finale performance at Main Quad.
“Mausoleum Party”: An annual Halloween Party at the Stanford Mausoleum, the final resting place of Leland Stanford Jr. and his parents. A 20-year tradition, the “Mausoleum Party” was on hiatus from 2002 to 2005 due to a lack of funding, but was revived in 2006. In 2008, it was hosted in Old Union rather than at the actual Mausoleum, because rain prohibited generators from being rented. In 2009, after fundraising efforts by the Junior Class Presidents and the ASSU Executive, the event was able to return to the Mausoleum despite facing budget cuts earlier in the year.
Former campus traditions include the “Big Game bonfire” on Lake Lagunita (a seasonal lake usually dry in the fall), which was formally ended in 1997 because of the presence of endangered salamanders in the lake bed.
Award laureates and scholars
Stanford’s current community of scholars includes:
Many Nobel Prize laureates
Many members of the National Academy of Sciences
Many members of National Academy of Engineering
Many members of National Academy of Medicine
A large number of members of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
Many recipients of the National Medal of Science and the National Medal of Technology
Recipients of the National Humanities Medal
Members of American Philosophical Society
Fellows of the American Physics Society (since 1995)
A number of Pulitzer Prize winners
A large number of MacArthur Fellows
Some Wolf Foundation Prize winners
A Few ACL Lifetime Achievement Award winners
A number of AAAI fellows
Some Presidential Medal of Freedom winners




