17 August 2018
Mary Halton

“As a kid… I never really thought there was a job where you worked on spacecraft.” Farah Alibay
Sending missions to Mars for a living sounds like a dream job. But not every day can be launch day – so what do Nasa’s spacecraft engineers get up to the rest of the time?
Dr Farah Alibay is based at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and works on the InSight mission – which lifted off to Mars in May 2018.

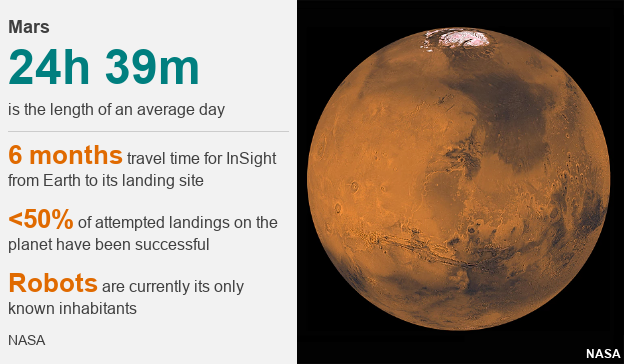
It aims to land on the planet in November and have a look inside – taking its internal temperature and listening for “Marsquakes” to learn more about how our nearest neighbour formed.
Now halfway to the Red Planet and running to a Mars day rather than an Earth one, InSight is looked after by a dedicated team who regularly check in with the spacecraft on its long journey, including Dr Alibay.
She shared a day at her job with the BBC.
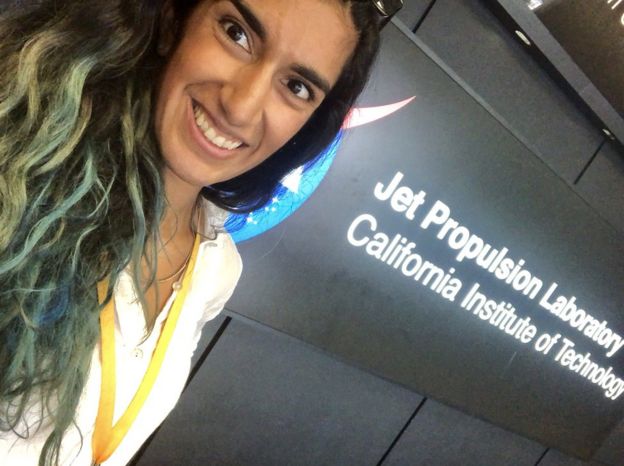

“My official title is Payload Systems Engineer.” Farah Alibay/JPL/NASA
What’s a working day like for you?
So it’s sort of weird that we’re on our way to Mars… and it’s really boring! But really that’s the way you want it to be. Everything’s going fine, so we’ll just keep going!
Before we launched, my job was to make sure that all the instruments were integrated properly on the spacecraft, and that they were tested properly.
Right now while we’re sort of in this limbo time where we’re waiting, my job is to help the teams prepare for operations.

“I love that a lot of my work is collaborative, so I spend a lot of time working with other people.” Farah Alibay/JPL/NASA
It’s kind of an engineer’s job to worry. Because it’s always the things you never imagined would happen that happen.
We’re halfway to Mars right now, literally this week is the halfway point, and I’ve been getting Mars landing nightmares.
Less than half the missions that have tried landing on Mars have succeeded. So it’s a little scary when you spend that much time on a spacecraft and it’s all going to come down to that one day – Monday 16 November. We’ll see what happens!
The way that we operate the spacecraft is that we basically write commands. Each one is a piece of code that we send up to the spacecraft to tell it what to do when it’s on the ground.
When the spacecraft is sleeping at night, we work. So we get all the data down, look at it and tell the spacecraft: “Hey InSight, tomorrow these are the tasks I want you to do!”
And then we uplink it, right before it wakes up in the morning. Then we go to bed and the spacecraft does its work.

Being ‘on console’ means working from mission control, home to the Deep Space Network which communicates with Nasa’s distant missions. Farah Alibay/JPL/NASA
But because the Mars day shifts every day, we also have to shift our schedule by an hour every day. So the first day we’ll start at 6am, and then [the next] will be 7am… 8am… 9am… and then we take a day off.
About once a week we’ve been turning on a different instrument and doing a checkout. So just making sure that everything was ok from launch, that the instrument is still behaving properly.
One of those tests is happening today. We do that from console because the spacecraft is being operated at Lockheed Martin in Denver, and the instrument teams are looking at that data from Europe, so we use a system that allows us all to talk to each other.
What’s your favourite aspect of your job?
No matter what I do on a given day, no one’s really done it before. And I think that’s what’s exciting. We don’t just do incremental change, we do brand new things.

Landing sites are carefully chosen, as many of the spacecraft that have tried to land on Mars have met with an unpleasant end. Farah Alibay/JPL/NASA
It helps put things in perspective, because my job does involve spending days looking at spreadsheets sometimes, or building PowerPoint slides, or answering emails. I definitely do a lot of that, so it’s just as boring sometimes as other jobs.
But putting it into perspective… even on a boring day my spacecraft is still on its way to Mars!
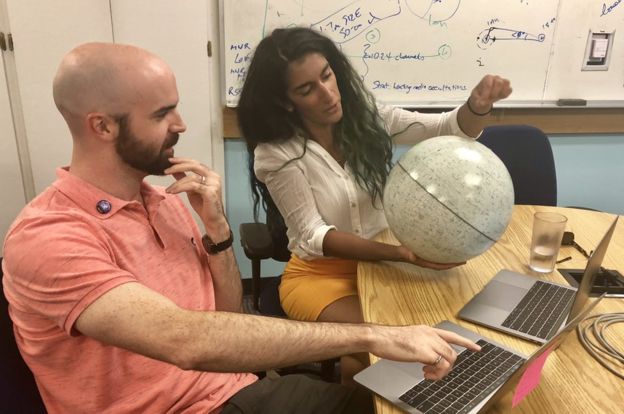

Team X brainstorm: “You can go to them and say I have this wild idea, and they make you make this wild idea into a mission concept.” Farah Alibay/JPL/NASA
How did you become a Nasa engineer?
So my path is a little strange. I actually grew up in England… I grew up in Manchester and went to university at Cambridge and then ended up at MIT. When I was at MIT I interned at JPL.
One of the things I try to do is mentor other women interns, because I had really great mentors when I was an intern, and that’s how I got my job.
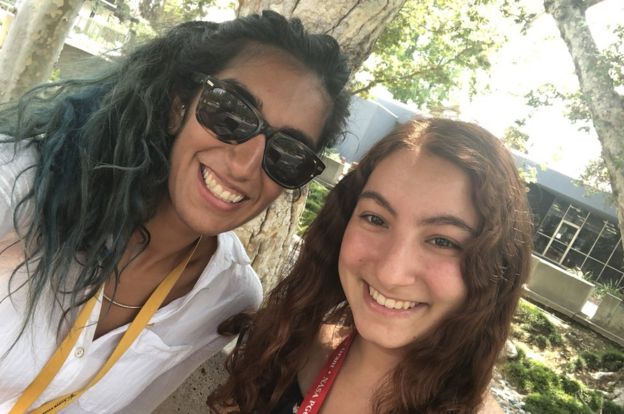

Dr Alibay with JPL intern Taleen Sarkissian.Farah Alibay/JPL/NASA
What’s next, after Mars?
I will be part of the InSight team until the end of the instrument deployment, so probably until February 2019.
My dream actually… we don’t have a mission on that yet, but my favourite moon is Saturn’s Enceladus.
The geysers at the south pole of Enceladus are incredible, and I’ve worked on mission concepts before that we’ve proposed to Nasa to fly through those plumes. One day I want there to be a mission to do that.
We’re focused on finding life in the Solar System right now, and I think a lot of us believe that in our lifetime… if there’s life in the Solar System we’re probably going find it.
So I want to be part of the team that finds it.
See the full article here .
five-ways-keep-your-child-safe-school-shootings
Please help promote STEM in your local schools.
Science Node is an international weekly online publication that covers distributed computing and the research it enables.
“We report on all aspects of distributed computing technology, such as grids and clouds. We also regularly feature articles on distributed computing-enabled research in a large variety of disciplines, including physics, biology, sociology, earth sciences, archaeology, medicine, disaster management, crime, and art. (Note that we do not cover stories that are purely about commercial technology.)
In its current incarnation, Science Node is also an online destination where you can host a profile and blog, and find and disseminate announcements and information about events, deadlines, and jobs. In the near future it will also be a place where you can network with colleagues.
You can read Science Node via our homepage, RSS, or email. For the complete iSGTW experience, sign up for an account or log in with OpenID and manage your email subscription from your account preferences. If you do not wish to access the website’s features, you can just subscribe to the weekly email.”


