From The Goddard Space Flight Center
And
The NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
6.6.24 [Just today from the institutions]
Jonathan Deal
Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala.
256-544-0034
jonathan.e.deal@nasa.gov

A red giant star and white dwarf orbit each other in this animation of a nova similar to T Coronae Borealis. The red giant is a large sphere in shades of red, orange, and white, with the side facing the white dwarf the lightest shades. The white dwarf is hidden in a bright glow of white and yellows, which represent an accretion disk around the star. A stream of material, shown as a diffuse cloud of red, flows from the red giant to the white dwarf. When the red giant moves behind the white dwarf, a nova explosion on the white dwarf ignites, creating a ball of ejected nova material shown in pale orange. After the fog of material clears, a small white spot remains, indicating that the white dwarf has survived the explosion. NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
Around the world this summer, professional and amateur astronomers alike will be fixed on one small constellation deep in the night sky. But it’s not the seven stars of Corona Borealis, the “Northern Crown,” that have sparked such fascination.
It’s a dark spot among them where an impending nova event – so bright it will be visible on Earth with the naked eye – is poised to occur.
“It’s a once-in-a-lifetime event that will create a lot of new astronomers out there, giving young people a cosmic event they can observe for themselves, ask their own questions, and collect their own data,” said Dr. Rebekah Hounsell, an assistant research scientist specializing in nova events at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “It’ll fuel the next generation of scientists.”
T Coronae Borealis, dubbed the “Blaze Star” and known to astronomers simply as “T CrB,” is a binary system nestled in the Northern Crown some 3,000 light-years from Earth. The system is comprised of a white dwarf – an Earth-sized remnant of a dead star with a mass comparable to that of our Sun – and an ancient red giant slowly being stripped of hydrogen by the relentless gravitational pull of its hungry neighbor.
The hydrogen from the red giant accretes on the surface of the white dwarf, causing a buildup of pressure and heat. Eventually, it triggers a thermonuclear explosion big enough to blast away that accreted material. For T CrB, that event appears to reoccur, on average, every 80 years.
Don’t confuse a nova with a supernova, a final, titanic explosion that destroys some dying stars, Hounsell said. In a nova event, the dwarf star remains intact, sending the accumulated material hurtling into space in a blinding flash. The cycle typically repeats itself over time, a process which can carry on for tens or hundreds of thousands of years.
“There are a few recurrent novae with very short cycles, but typically, we don’t often see a repeated outburst in a human lifetime, and rarely one so relatively close to our own system,” Hounsell said. “It’s incredibly exciting to have this front-row seat.”
Finding T Coronae Borealis

A conceptual image of how to find Hercules and the “Northern Crown” in the night sky, created using planetarium software. Look up after sunset during summer months to find Hercules, then scan between Vega and Arcturus, where the distinct pattern of Corona Borealis may be identified. NASA
The first recorded sighting of the T CrB nova was more than 800 years ago, in autumn 1217, when a man named Burchard, abbot of Ursberg, Germany, noted his observance of “a faint star that for a time shone with great light.”
The T CrB nova was last seen from Earth in 1946. Its behavior over the past decade appears strikingly similar to observed behavior in a similar timeframe leading up to the 1946 eruption. If the pattern continues, some researchers say, the nova event could occur by September 2024.
What should stargazers look for? The Northern Crown is a horseshoe-shaped curve of stars west of the Hercules constellation, ideally spotted on clear nights. It can be identified by locating the two brightest stars in the Northern Hemisphere – Arcturus and Vega – and tracking a straight line from one to the other, which will lead skywatchers to Hercules and the Corona Borealis.
The outburst will be brief. Once it erupts, it will be visible to the naked eye for a little less than a week – but Hounsell is confident it will be quite a sight to see.
A coordinated scientific approach
Watch V407 Cyg go nova! In this animation, gamma rays (magenta) arise when accelerated particles in the explosion’s shock wave crash into the red giant’s stellar wind. NASA/Conceptual Image Lab/Goddard Space Flight Center
Dr. Elizabeth Hays, chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory at NASA Goddard, agreed. She said part of the fun in preparing to observe the event is seeing the enthusiasm among amateur stargazers, whose passion for extreme space phenomena has helped sustain a long and mutually rewarding partnership with NASA.
“Citizen scientists and space enthusiasts are always looking for those strong, bright signals that identify nova events and other phenomena,” Hays said. “Using social media and email, they’ll send out instant alerts, and the flag goes up. We’re counting on that global community interaction again with T CrB.”
Hays is the project scientist for NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, which has made gamma-ray observations from low Earth orbit since 2008.


Fermi is poised to observe T CrB when the nova eruption is detected, along with other space-based missions including Webb, Swift, IXPE, NuSTAR, NICER, and the European Space Agency’s INTEGRAL.






Numerous ground-based radio telescopes and optical imagers, including the National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s Very Large Array in New Mexico, also will take part. Collectively, the various telescopes and instruments will capture data across the visible and non-visible light spectrum.

See the full article here.
Comments are invited and will be appreciated, especially if the reader finds any errors which I can correct.

five-ways-keep-your-child-safe-school-shootings
Please help promote STEM in your local schools.
The NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s capabilities and experience are essential to nearly every facet of NASA’s mission of exploration and discovery.
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Huntsville, Alabama, is the U.S. government’s civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, The NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s first mission was developing the Saturn launch vehicles for the Apollo program. Marshall has been the lead center for the Space Shuttle main propulsion and external tank; payloads; and related crew training; International Space Station (ISS) design and assembly; computers, networks, and information management; and the Space Launch System (SLS). Located on the Redstone Arsenal near Huntsville, The NASA Marshall Space Flight Center is named in honor of General of the Army George C. Marshall.
The center contains the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC), also known as the International Space Station Payload Operations Center. This facility supports ISS launch; payload and experiment activities at the Kennedy Space Center. The HOSC also monitors rocket launches from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station when a Marshall Center payload is on board.
Since that time, most U.S. space exploration efforts have been led by NASA, including the Apollo moon-landing missions, the Skylab space station, and later the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA is supporting the International Space Station and is overseeing the development of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and Commercial Crew vehicles. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program (LSP) which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for unmanned NASA launches. Most recently, NASA announced a new Space Launch System that it said would take the agency’s astronauts farther into space than ever before and lay the cornerstone for future human space exploration efforts by the U.S.
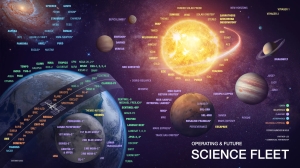
NASA science is focused on better understanding Earth through the Earth Observing System, advancing heliophysics through the efforts of the Science Mission Directorate’s Heliophysics Research Program, exploring bodies throughout the Solar System with advanced robotic missions such as New Horizons, and researching astrophysics topics, such as the Big Bang, through the Great Observatories [NASA/ESA Hubble, NASA Chandra, NASA Spitzer, and associated programs.] NASA shares data with various national and international organizations such as from [JAXA]Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite.

The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD is home to the nation’s largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
Named for American rocketry pioneer Dr. Robert H. Goddard, the center was established in 1959 as NASA’s first space flight complex. Goddard and its several facilities are critical in carrying out NASA’s missions of space exploration and scientific discovery.
GSFC also operates two spaceflight tracking and data acquisition networks (the NASA Deep Space Network and the Near Earth Network); develops and maintains advanced space and Earth science data information systems, and develops satellite systems for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
GSFC manages operations for many NASA and international missions including the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope; the Explorers Program; the Discovery Program; the Earth Observing System; INTEGRAL; MAVEN; OSIRIS-REx; the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory ; the Solar Dynamics Observatory; Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System ; Fermi; and Swift. Past missions managed by GSFC include the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE), Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, SMM, COBE, IUE, and ROSAT. Typically, unmanned Earth observation missions and observatories in Earth orbit are managed by GSFC, while unmanned planetary missions are managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California.
Goddard is one of four centers built by NASA since its founding on July 29, 1958. It is NASA’s first, and oldest, space center. Its original charter was to perform five major functions on behalf of NASA: technology development and fabrication; planning; scientific research; technical operations; and project management. The center is organized into several directorates, each charged with one of these key functions.
Until May 1, 1959, NASA’s presence in Greenbelt, MD was known as the Beltsville Space Center. It was then renamed the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), after Robert H. Goddard. Its first 157 employees transferred from the United States Navy’s Project Vanguard missile program, but continued their work at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C., while the center was under construction.
Goddard Space Flight Center contributed to Project Mercury, America’s first manned space flight program. The Center assumed a lead role for the project in its early days and managed the first 250 employees involved in the effort, who were stationed at Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. However, the size and scope of Project Mercury soon prompted NASA to build a new Manned Spacecraft Center, now the Johnson Space Center, in Houston, Texas. Project Mercury’s personnel and activities were transferred there in 1961.
The Goddard network tracked many early manned and unmanned spacecraft.
Goddard Space Flight Center remained involved in the manned space flight program, providing computer support and radar tracking of flights through a worldwide network of ground stations called the Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network (STDN). However, the Center focused primarily on designing unmanned satellites and spacecraft for scientific research missions. Goddard pioneered several fields of spacecraft development, including modular spacecraft design, which reduced costs and made it possible to repair satellites in orbit. Goddard’s Solar Max satellite, launched in 1980, was repaired by astronauts on the Space Shuttle Challenger in 1984. The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, remains in service and continues to grow in capability thanks to its modular design and multiple servicing missions by the Space Shuttle.
Today, the center remains involved in each of NASA’s key programs. Goddard has developed more instruments for planetary exploration than any other organization, among them scientific instruments sent to every planet in the Solar System. The center’s contribution to the Earth Science Enterprise includes several spacecraft in the Earth Observing System fleet as well as EOSDIS, a science data collection, processing, and distribution system. For the manned space flight program, Goddard develops tools for use by astronauts during extra-vehicular activity, and operates the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, a spacecraft designed to study the Moon in preparation for future manned exploration.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation’s civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research.

President Dwight D. Eisenhower established the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1958 with a distinctly civilian (rather than military) orientation encouraging peaceful applications in space science. The National Aeronautics and Space Act was passed on July 29, 1958, disestablishing NASA’s predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). The new agency became operational on October 1, 1958.
Since that time, most U.S. space exploration efforts have been led by NASA, including the Apollo moon-landing missions, the Skylab space station, and later the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA is supporting the International Space Station and is overseeing the development of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and Commercial Crew vehicles. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program (LSP) which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for unmanned NASA launches. Most recently, NASA announced a new Space Launch System that it said would take the agency’s astronauts farther into space than ever before and lay the cornerstone for future human space exploration efforts by the U.S.




